Data privacy and compliance framework
We may describe our period as one of overwhelming knowledge which provides enormous potential value and peril. Some of the most valuable information accessible concerns persons such as health, finances, jobs, history of purchases, relations, etc. New organizations that want to acquire this confidential info while at the same time lowering related risk must create a compromise between creativity and assistance on the one hand and consumer confidence on another. For ordinary operations, that problem poses several questions: Where are the privacy duties of my organization, and can we show them our responsibility? Do we know clearly, by whom and for what purposes, what personal data are processed? Are our personal data properly protected? Are we willing to respond completely to a system breach?
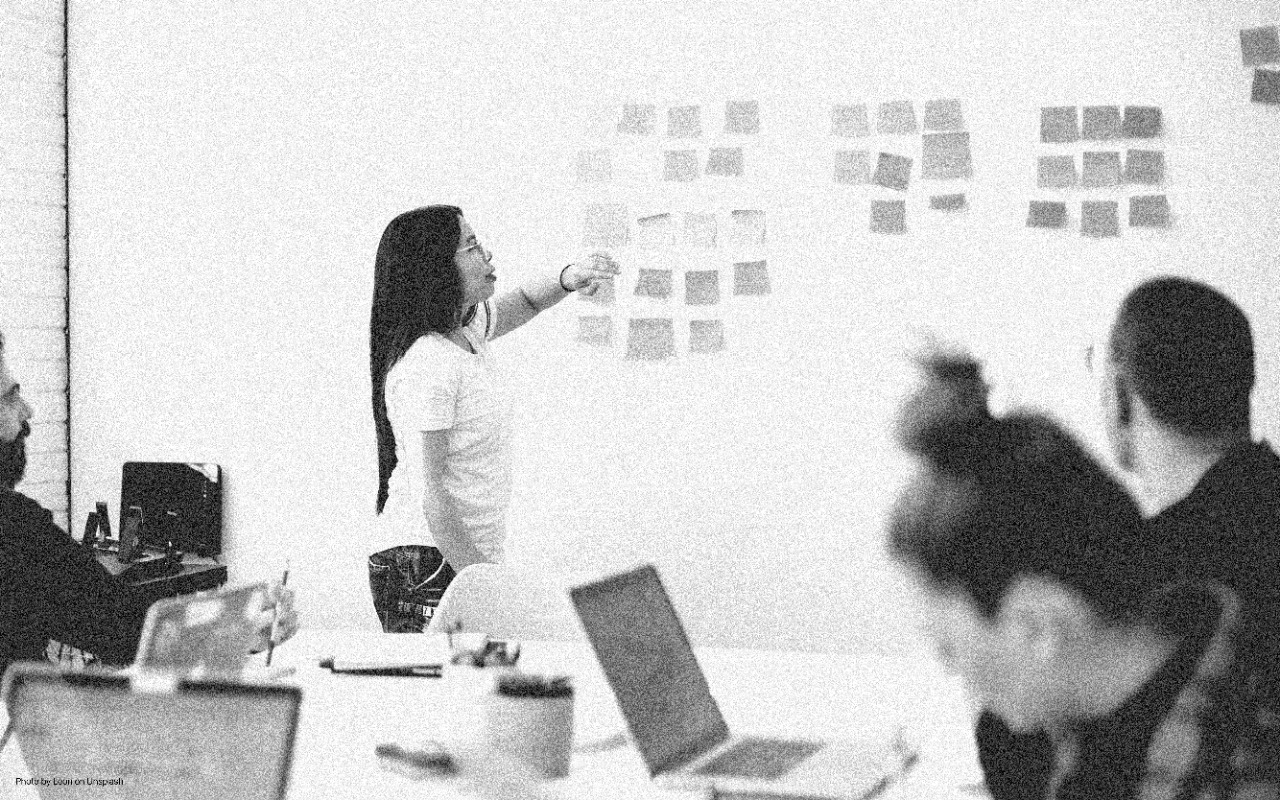




In the process of adopting Data Protection Act the Indonesian House of Representatives will require the Regulation Act to concern with :
- Protection of data is always a difficulty, but when the data takes the shape of a valued, concentrated target, it becomes harder.
- A “right to delete” involves the deletion of previously supplied personal information, including third parties’ use of this data. This is a difficulty in the context of big data, because there are numerous forms and copies of data, and frequently inadequate anonymisation.
- Retaining the original (intended) purpose of data that can greatly diminish the value of Big Data analysis for new and inventive secondary purposes for the reuse of data.
- As a general concept, data reduction goes against the emphasis of big data on data processing and analysis.
What Meta Lab Can Help?


Privacy Response


Privacy by Design:DPIA


Privacy Strategy and Governance

Data Compliance and internal control process :GDPR, HIPAA, Sunshine Act, Legal Compliance

